 Guidelines for Industries
Guidelines for Industries
 The
APPCB follows a set of guidelines in granting Consent for establishment
to different industries. The guidelines that different industries have
to follow are given below based on the Industry type. Please click on
your relevant industry to access guidelines.
The
APPCB follows a set of guidelines in granting Consent for establishment
to different industries. The guidelines that different industries have
to follow are given below based on the Industry type. Please click on
your relevant industry to access guidelines.
 Guidelines for Cement Grinding Units :
Guidelines for Cement Grinding Units :
 These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
 These
siting guidelines are not applicable for the units proposed in the
IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and for expansion of the existing
units.
These
siting guidelines are not applicable for the units proposed in the
IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and for expansion of the existing
units.
 The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
| Orange (Total investment upto Rs. 10 Crores) |
25 m |
20 m |
10 m |
The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
- Vehicle parking.
- Administrative building and security office.
- Green belt.
- Electrical Substation / transformers.
- Fuel Station.
- Water supply sumps and
- Other non-industrial activities.
 The
distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation,
educational institutions and religious places shall not be less than 300
m.
The
distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation,
educational institutions and religious places shall not be less than 300
m.
 Minimum area of the site shall be Ac. 1.5.
Minimum area of the site shall be Ac. 1.5.
 Greenbelt
shall be developed along the boundary of the land, with atleast two
rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus (Dubai plants) etc., to
act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution.
Greenbelt
shall be developed along the boundary of the land, with atleast two
rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus (Dubai plants) etc., to
act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution.
 Bag filter for grinding unit and cement silo shall be provided.
Bag filter for grinding unit and cement silo shall be provided.
 Stone Crushing Units
Stone Crushing Units
 These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
 These
siting guidelines are not applicable for the units proposed in the
IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and for expansion of the existing
units.
These
siting guidelines are not applicable for the units proposed in the
IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and for expansion of the existing
units.
 The distance between the boundary of the site and boundary of the
The distance between the boundary of the site and boundary of the
i) National Highway shall be -500 m
ii) State High way, MDR and other roads shall be -100 m
The distance between the
boundary of the site and human habitation, educational institutions and
religious places shall not be less than 500 m.
Preferably located near the quarries.
 Minimum area of land required – 3 acres.
Minimum area of land required – 3 acres.
 Green belt of width 5 m shall be developed along the boundary of the
land, with atleast three rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus
(Dubai plants) etc., to act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution. A
barricade with steel sheets shall be provided between the Crusher area
and the green belt. The height of the barricade shall be 1.0 metre above
the highest point of the stone crusher / conveyor belt.
Green belt of width 5 m shall be developed along the boundary of the
land, with atleast three rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus
(Dubai plants) etc., to act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution. A
barricade with steel sheets shall be provided between the Crusher area
and the green belt. The height of the barricade shall be 1.0 metre above
the highest point of the stone crusher / conveyor belt.


 Dairy Units (except Chilling units)
Dairy Units (except Chilling units)
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are not applicable for
the units proposed in the IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and for
expansion of the existing units.
 The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
| 1 |
Red (integrated) |
50 m |
40 m |
20 m |
| 2 |
Orange (small scale) |
25 m |
20 m |
10 m |
 The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
- Vehicle parking.
- Administrative building and security office
- Green belt.
- Electrical Substation / transformers.
- Fuel Station.
- Water supply sumps and
- Other non-industrial activities.
The distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation,
educational institutions and religious places shall not be less than 300
m.
 Area of the green belt shall be @ one acre to dispose 10 KLD of treated waste water, in addition to the built-up area. (OR)
Area of the green belt shall be @ one acre to dispose 10 KLD of treated waste water, in addition to the built-up area. (OR)
 The
industry can discharge the treated effluents into surrounding fields,
after submitting the NOC from the farmers to the Board.
The
industry can discharge the treated effluents into surrounding fields,
after submitting the NOC from the farmers to the Board.
- New Dairy units shall install bag filters as the control equipment
for the boiler(s), if the distance between the boundary of the site and
human habitation, educational institutions and religious places is less
than 500 m.
- If, the distance between the boundary of the site of the new Dairy
units and human habitation, educational institutions and religious
places is equal to or more than 500 m, cyclone / multi-cyclones are
sufficient as the control equipment for the boiler(s).
- If the fuel for the boiler is oil such as diesel, pollution control
equipment is not required. Required stack height shall be provided.
 LPG Bottling Unit (Upto 100 tonnes storage)
LPG Bottling Unit (Upto 100 tonnes storage)
 The distance between the boundary of the site and boundary of any road shall be at least 100 m.
The distance between the boundary of the site and boundary of any road shall be at least 100 m.
 The distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation (boundary of Town, Village etc.) shall be at least 1 km.
The distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation (boundary of Town, Village etc.) shall be at least 1 km.
 Total area of land acquired – Ac. 5.0
Total area of land acquired – Ac. 5.0
 On site emergency plan to be prepared before the activity is commenced i.e. before the trial production.
On site emergency plan to be prepared before the activity is commenced i.e. before the trial production.

 Cashew Processing Unit
Cashew Processing Unit
Drum Process
 To be located 1 km away from habitation
To be located 1 km away from habitation
 No new units to be allowed in Palasa, Kasibugga & Mogilipadu.
No new units to be allowed in Palasa, Kasibugga & Mogilipadu.
 Distance between 2 units shall be 500 m.
Distance between 2 units shall be 500 m.
 A distance of 500 m shall be maintained between the boundary of site and the edge of National & State Highway.
A distance of 500 m shall be maintained between the boundary of site and the edge of National & State Highway.
 A distance of 100 m shall be maintained from boundary of site and Edge of B.T. Roads in the Districts.
A distance of 100 m shall be maintained from boundary of site and Edge of B.T. Roads in the Districts.
 Boiling Process (modified guidelines)
Boiling Process (modified guidelines)
In the 5th Board Meeting held on 20.04.2017
vide Resolution No. 97/2017, the Board approved the following revised
guidelines for establishment of new Cashew Nut Processing Units:
 To be located 200 m away from habitation.
To be located 200 m away from habitation.
 No
new units to be allowed in Palasa, Kasibugga and Mogilipadu clusters.
However, new unit with boiling process will be allowed replacing sick
unit in the said clusters where roasting process took place hitherto on
submission of the proof of the existence of the old unit from any of the
Government departments. Multiple new units in one premises, in place of
one sick unit is not allowed.
No
new units to be allowed in Palasa, Kasibugga and Mogilipadu clusters.
However, new unit with boiling process will be allowed replacing sick
unit in the said clusters where roasting process took place hitherto on
submission of the proof of the existence of the old unit from any of the
Government departments. Multiple new units in one premises, in place of
one sick unit is not allowed.
 De-oiled cashew nut shell / bio-mass shall be used as fuel for the boiler and drier.
De-oiled cashew nut shell / bio-mass shall be used as fuel for the boiler and drier.
 Guidelines for Pulverizing Units:
Guidelines for Pulverizing Units:
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are not applicable for
the units proposed in the IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and for
expansion of the existing units.
 The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
 The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
- Vehicle parking.
- Administrative building and security office.
- Green belt.
- Electrical Substation / transformers.
- Fuel Station.
- Water supply sumps and
- Other non-industrial activities.
 The minimum distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation shall be 300 m.
The minimum distance between the boundary of the site and human habitation shall be 300 m.
 Minimum area of the site shall be Ac. 1.5.
Minimum area of the site shall be Ac. 1.5.
 Greenbelt
shall be developed along the boundary of the land, with atleast two
rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus (Dubai plants) etc., to
act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution.
Greenbelt
shall be developed along the boundary of the land, with atleast two
rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus (Dubai plants) etc., to
act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution.
 Bag filter has to be provided for the pulverizer.
Bag filter has to be provided for the pulverizer.


 Para Boiling Rice Mills
Para Boiling Rice Mills
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are not applicable
for the units proposed in the IEs/IDAs/Industrial Parks/ SEZ etc., and
for expansion of the existing units.
 The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
The width of buffer zone to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
| 1 |
Red (wastewater generation > 100 KLD or fuel
consumption > 12 MTD or both ) |
50 m |
40 m |
20 m |
| 2 |
Orange (wastewater generation < 100 KLD or fuel consumption < 12 MTD or both ) |
25 m |
20 m |
10 m |
 The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
- Vehicle parking.
- Administrative building and security office.
- Green belt.
- Electrical Substation / transformers.
- Fuel Station.
- Water supply sumps and
- Other non-industrial activities.
 The distance
between the boundary of the site and human habitation, educational
institutions and religious places shall not be less 300 m.
The distance
between the boundary of the site and human habitation, educational
institutions and religious places shall not be less 300 m.
 The new units shall not be located in the catchment area of drinking water source.
The new units shall not be located in the catchment area of drinking water source.
 Area of the green belt shall be @ one acre to dispose 10 KLD of treated waste water, in addition to the built-up area. (OR)
Area of the green belt shall be @ one acre to dispose 10 KLD of treated waste water, in addition to the built-up area. (OR)
 The
industry can discharge the treated effluents into surrounding fields,
after submitting the NOC from the farmers to the Board.
The
industry can discharge the treated effluents into surrounding fields,
after submitting the NOC from the farmers to the Board.
 Greenbelt
shall be developed along the boundary of the land, with atleast two
rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus (Dubai plants) etc., to
act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution.
Greenbelt
shall be developed along the boundary of the land, with atleast two
rows of tall growing plants such as Conocarpus (Dubai plants) etc., to
act as a barrier to mitigate dust pollution.
 Rice
Husk / Boiler ash shall be stored in a separate closed sheds in one of
the corners of the site, away from habitation, educational institutions
and religious places and roads.
Rice
Husk / Boiler ash shall be stored in a separate closed sheds in one of
the corners of the site, away from habitation, educational institutions
and religious places and roads.
 Bag
filter shall be provided to the Boiler. If the fuel for the boiler is
oil such as diesel, pollution control equipment is not required.
Required stack height shall be provided.
Bag
filter shall be provided to the Boiler. If the fuel for the boiler is
oil such as diesel, pollution control equipment is not required.
Required stack height shall be provided.

 Pesticide Formulation Units
Pesticide Formulation Units
 No clusters of pesticide formulation units shall be permitted.
No clusters of pesticide formulation units shall be permitted.
 The
quality of product (after mixing) shall be ensured and certified by
agricultural department before going into commercial production. The
certificate shall be produced before the APPCB while applying for CFO or
when the unit goes for expansion.
The
quality of product (after mixing) shall be ensured and certified by
agricultural department before going into commercial production. The
certificate shall be produced before the APPCB while applying for CFO or
when the unit goes for expansion.
 The
proponent has to substantiate the break-up the capital cost so that a
proportionate amount is justified for pollution control measures for
odour or dust causing products /processes.
The
proponent has to substantiate the break-up the capital cost so that a
proportionate amount is justified for pollution control measures for
odour or dust causing products /processes.
 The
solid, liquid and gaseous formulation units shall have extraction and
scrubbing systems for mitigation of smell or to avoid any accidental
leakages of poisonous gases.
The
solid, liquid and gaseous formulation units shall have extraction and
scrubbing systems for mitigation of smell or to avoid any accidental
leakages of poisonous gases.
 Bag filters shall be installed to trap particulate matter at all dust emission points in the process.
Bag filters shall be installed to trap particulate matter at all dust emission points in the process.
 Dry
mopping vacuum cleaning of floor shall be adopted instead of wet floor
washing and vessel cleaning as it prevents water contamination.
Dry
mopping vacuum cleaning of floor shall be adopted instead of wet floor
washing and vessel cleaning as it prevents water contamination.
 Solid waste/drums shall be detoxified and they only disposed off by incineration or to the scrap dealers.
Solid waste/drums shall be detoxified and they only disposed off by incineration or to the scrap dealers.
 The unit shall be located at least a raidal distance of 1 km away from any human habitation excluding APIIC IEs/IDAs.
The unit shall be located at least a raidal distance of 1 km away from any human habitation excluding APIIC IEs/IDAs.
 All odour causing chemicals in the formulation units shall be stored in a separate place within the premises.
All odour causing chemicals in the formulation units shall be stored in a separate place within the premises.
 The units shall have at least 50-80% open area other than the factory built up area.
The units shall have at least 50-80% open area other than the factory built up area.
 Sponge Iron Units – Guidelines / Code of practice for Pollution prevention for Sponge Iron Plants (CPCB)
Sponge Iron Units – Guidelines / Code of practice for Pollution prevention for Sponge Iron Plants (CPCB)
Air Pollution
 Stack Emission from Kiln
Stack Emission from Kiln
i)
Adequately designed ESP or any other adequate air pollution control
system/combination of system should be installed to achieve the
prescribed stack emission standards
As
installation and operation of Pollution Control Equipment for plants
with less than 100 TPD capacity is not economically viable, therefore,
it is recommended that plants with less than 100 TPD shall not be
permitted in future.
Program for phasing out old plants having capacity less than 100 TPD shall be worked out by the State Pollution Control Board.
ii)
All Pollution control equipment should be provided with separate
electricity meter and totaliser for continuous recording of power
consumption. The amperage of the ID fan should also be recorded
continuously. Non-functioning of Pollution control equipment should be
recorded in the same logbook along with reasons for not running the
Pollution Control Equipment.
iii)
The safety cap/emergency stack of rotary kiln type plant, which is
generally installed above the After Burner Chamber (ABC) of feed end
column should not be used for discharging untreated emission, bypassing
the air pollution control device.
iv)
In order to prevent bypassing of emissions through safety cap and
non-operation of ESP or any other pollution control device, software
controlled interlocking facility should be provided on the basis of real
time data from the plant control system, to ensure stoppage of feed
conveyor, so that, feed to the kiln would stop automatically, if safety
cap of the rotary kiln is opened or ESP is not in operation. The system
should be able to take care of multiple operating parameters and their
inter relations to prevent any possibility of defeating the basic
objective of the interlock. The system should be foolproof to prevent
any kind of tempering. The software based interlocking system, proposed
to be installed by industry should be get approved by the concerned
State Pollution Control Board, for its adequacy, before installation by
the industry.
v)
Mechanical operated system for timely collection and removal of the
flue dust generated in ESP or any other pollution control device shall
be installed.
 Stack Emission from de-dusting units
Stack Emission from de-dusting units
All
de-dusting units should be connected to a stack having a minimum stack
height of 30 m. Sampling porthole and platform etc. shall be provided as
per CPCB emission regulation to facilitate stack monitoring. De-dusting
units can also be connected to ABC Chamber and finally emitted through
common stack with kiln off-gas emissions.
 Fugitive Emission
Fugitive Emission
The
measurement may be done, preferably on 8-hour basis with high volume
sampler. However, depending upon the prevalent conditions at the site,
the period of measurement can be reduced.
 Effluent Discharge
Effluent Discharge
All efforts should be made to reuse and re-circulate the water and to maintain zero effluent discharge.
Storm water / garland drain should be provided in the plant.
 Noise Control
Noise Control
The industry should take measures to
control the Noise Pollution so that the noise level standards already
notified for Industrial area are complied.
 Solid Waste Management
Solid Waste Management
Char
Char should be mixed with coal or coal washery rejects and used
as fuel in Fluidized Bed Combustion Boilers (FBC) for generation of
power. The plants having capacity 200 TPD and above should install
Fluidized Bed Combustion Boilers (FBC) for generation of power. Also the
smaller capacity individual Sponge Iron Plants (Capacity upto 100 TPD)
and operating in cluster can collectively install common Fluidized Bed
Combustion Boilers (FBC) for power generation. The Sponge Iron Plant are
free to explore other options / possibilities to use char for
generation of power. Char can be sold to local entrepreneurs for making
coal briquettes. It can also be mixed with coal fines, converted to
briquettes and used in brick kilns.
Under no
circumstances char should be disposed off in agricultural fields/other
areas. Logbook for daily record, of Char production and usage must be
maintained by the industry and the record shall be made available to
officials of CPCB/SPCB/PCC during inspection.
Kiln Accretions
The kiln accretions are heavy solid lumps and can be used as
sub- base material for road construction or landfill, after ascertaining
the composition for its suitability and ensuring that it should not
have any adverse environmental impact.
Gas Cleaning Plant (GCP)/Scrubber Sludge
The sludge should be compacted and suitably disposed off after
ascertaining the composition for its suitability and ensuring that it
should not have any adverse environmental impact.
Flue Dust / Fly ash
Flue dust is generated from air pollution control system i.e.
ESP or any other air pollution control system installed with kiln.
Secondary flue dust is also generated from Bag Filters or any other air
pollution control equipment installed with Raw Material Handling, Coal
Crusher, Cooler Discharge and Product house unit. The reuse/ recycling
of the flue dust generated / collected may be explored and suitably
implemented.
Fly ash brick
manufacturing plant should be install for fly ash utilization. Fly ash
can be utilized in cement making by Cement industry also.
Bottom Ash
Bottom ash may have objectionable metallic compounds, therefore
should be stored in properly designed landfills as per CPCB guidelines
to prevent leaching to the sub-soil and underground aquifer.
General
Solid waste management program should be prepared with thrust
on reuse and recycling. Solid waste disposal site should be earmarked
within the plant premises. The storage site of solid waste should be
scientifically designed keeping in view that the storage of solid waste
should not have any adverse impact on the air quality or water regime,
in any way.
The various types of
solid wastes generated should be stored separately as per CPCB
guidelines so that it should not adversely affect the air quality,
becoming air borne by wind or water regime during rainy season by
flowing along with the storm water.


 Raw Material handling and Preparation
Raw Material handling and Preparation
i) Unloading
of coal by trucks or wagons should be carried out with proper care
avoiding dropping of the materials from height. It is advisable to moist
the material by sprinkling water while unloading.
ii) Crushing
and screening operation should be carried out in enclosed area.
Centralized de- dusting facility (collection hood and suction
arrangements followed by de-dusting unit like bag filter or ESP or
equally effective method or wet scrubber and finally discharge of
emission through a stack) should be provided to control Fugitive
Particulate Matter Emissions. The stack should confirm to the emission
standards notified for de-dusting units. Water sprinkling arrangement
should be provided at raw material heaps and on land around the crushing
and screening units.
iii) Work area including the roads surrounding the plant shall be asphalted or concreted.
iv) Enclosure should be provided for belt conveyors and transfer points of belt conveyors.
The above enclosures shall be rigid and permanent (and not of flexible/
cloth type enclosures) and fitted with self- closing doors and close
fitting entrances and exits, where conveyors pass through the
enclosures. Flexible covers shall be installed at entry and exit of the
conveyor to the enclosures, minimizing the gaps around the conveyors.In
the wet system, water sprays/ sprinklers shall be provided at the
following strategic locations for dust suppression during raw material
transfer:
– Belt conveyor discharge/ transfer point
– Crusher/screen discharge locations
 Waste Heat Recovery Boiler (WHRB)
Waste Heat Recovery Boiler (WHRB)
Sponge Iron Plants of capacity more than 100 TPD kilns shall use Waste Heat Recovery
Boiler (WHRB) for generation of power.
 Cooler Discharge and Product Separation
Unit
Cooler Discharge and Product Separation
Unit
Permanent and rigid enclosures shall be provided for belt conveyors and transfer
points of belt conveyors. Dust extraction cum control system preferably bag filters
or ESP to arrest product loss in cooler discharge and product separation area shall
be installed.
 Char based Power Plant
Char based Power Plant
For plant having capacity of 200 TPD of cumulative kiln capacity, the power production
through FBC boiler using char as a part of fuel, is a viable option. Power generation
through FBC boiler using char as a part of fuel be implemented in a phased manner
within 4 years of commissioning and targeting for 100% utilization of char.
Individual Sponge Iron Plants of capacity upto 100 TPD and located in cluster can
install a common char based power plant collectively.
 New Sponge Iron Plants
New Sponge Iron Plants
i) No New Sponge Iron Plant will be commissioned without
installation of Pollution control systems as stipulated in the Standards. The concerned
State Pollution Control Board will accord consent to operate only after Physical
verification of the adequacy of the Installed pollution control systems for meeting
the standards and stipulated conditions in the consent to establish.
ii) All new kilns shall have the independent stack with the
kiln or multi-flue stacks in case two or more kilns are joining the same stack for
better dispersion of pollutants.
iii) Any entrepreneur having more than 2×100 TPD kiln may
install WHRB for power generation, as it’s a techno-economic viable option. For
plants having capacity of 200 TPD or more, power generation using char in FBC Boiler
as part of fuel is techno-economic viable option, therefore, new plants must install
FBC boiler for power generation at the time of installation of the industry.
iv) Any new sponge iron plant being installed along with
the other downstream facilities of converting the sponge iron into steel with/without
further processing the steel should meet the target of 100% utilization of sensible
heat of DR (Direct Reduction) Gas and Char for power generation. Wet scrubbing system
for kiln off-gas treatment for such plants should not be opted.
 General Guidelines
General Guidelines
i) Extensive plantation/Green belt shall be developed along
the roads and boundary line of the industry. A minimum 15 m width Green Belt along
the boundary shall be maintained. However, the green belt may be designed scientifically
depending upon the requirement and local and mix species of plants may be selected
for the green belt.
ii) Monitoring of stack emissions, fugitive emissions, trade
effluent and noise level shall be done as per CPCB regulations.
iii) Pollution control systems shall be operated as an integral
part of production to ensure minimum emissions. Pollution Control System shall
start before conveyor operation/operation of plant. Similarly pollution control
system shall be stopped only after completion of conveyor operation/operation of
plant so that possibility of dust settlement in ducts can be eliminated. Continuous
evacuation of dust (from Dust catchers, ESPs, Bag filter hopper etc.) shall be organized.
 Siting Guideline for Sponge Iron Plants
Siting Guideline for Sponge Iron Plants
Siting of new sponge iron plants shall be as per respective State Pollution
Control Board guidelines. However the following aspects shall also be considered:
i) Residential habitation (residential localities/ village)
and ecologically and/or otherwise sensitive areas: A minimum distance of at least
1000 m (1.0 km) to be maintained.
ii) The location of Sponge Iron Plant should be at least
500 m away from National Highway and State Highway .
iii) Radial distance between two Sponge Iron Plants should
be 5 km for plants having capacity 1000 TPD or more.
 Sitting Guidelines for Transportation / Communication
System
Sitting Guidelines for Transportation / Communication
System
 In the 5th Board Meeting
held on 20.04.2017 vide resolution no. 98/2017; the Board approved the following
revised guidelines with respect to distance between the industries and the roads:
In the 5th Board Meeting
held on 20.04.2017 vide resolution no. 98/2017; the Board approved the following
revised guidelines with respect to distance between the industries and the roads:
|
1
|
Red
|
50 m
|
40 m
|
20 m
|
|
2
|
Orange
|
25 m
|
20 m
|
10 m
|
|
3
|
Green
|
Exempted from the distance criteria.
|
 The buffer zone shall be permitted
to utilise for the following:
The buffer zone shall be permitted
to utilise for the following:
- Vehicle parking.
- Administrative building and security office.
- Green belt.
- Electrical Substation / transformers.
- Fuel Station.
- Water supply sumps and
- Other non-industrial activities.
 These guidelines shall be applicable
to industries other than those categories of industries for which specific guidelines
are formulated by the Board.
These guidelines shall be applicable
to industries other than those categories of industries for which specific guidelines
are formulated by the Board.
 These guidelines are not applicable
to the industries to be located within industrial estates.
These guidelines are not applicable
to the industries to be located within industrial estates.
 Tyre Pyrolysis units:
Tyre Pyrolysis units:
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto
Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are not applicable for the units proposed in the IEs/IDAs/Industrial
Parks/ SEZ etc., and for expansion of the existing units.
 The width of buffer zone
to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
The width of buffer zone
to be maintained from the Road Land Boundary to the industry shed shall be as following:
The buffer zone shall be permitted to utilise for the following:
- Vehicle parking.
- Administrative building and security office.
- Green belt.
- Electrical Substation / transformers.
- Fuel Station.
- Water supply sumps and
- Other non-industrial activities.
 Shall be located atleast 500 m away
from habitations.
Shall be located atleast 500 m away
from habitations.
 Burners shall be installed to flare
up excess non condensable gases with safety arrangements.
Burners shall be installed to flare
up excess non condensable gases with safety arrangements.
 Air pollution control equipment shall
be provided to control the flue gas emissions generated during the heating of the
Pyrolysis reactor.
Air pollution control equipment shall
be provided to control the flue gas emissions generated during the heating of the
Pyrolysis reactor.
 No further distillation of oil shall
be carried out.
No further distillation of oil shall
be carried out.
 The by-products, carbon black
shall be collected properly and stored in closed shed without causing any spillages
before selling to outside parties.
The by-products, carbon black
shall be collected properly and stored in closed shed without causing any spillages
before selling to outside parties.
 Solvent Recovery units:
Solvent Recovery units:
These siting guidelines are applicable to the units with total investments upto
Rs. 10.0 Crores.
These siting guidelines are not applicable for the units proposed in the IEs/IDAs/Industrial
Parks/ SEZ etc., and for expansion of the existing units.
 The solvent recovery units shall
be installed in Industrial Estates / industrial parks / IDAs / SEZs.
The solvent recovery units shall
be installed in Industrial Estates / industrial parks / IDAs / SEZs.
 The solvent recovery units shall
dispose the inorganic hazardous waste to TSDF for land filling and organic residue
to TSDF for incineration / cement plants for co-processing.
The solvent recovery units shall
dispose the inorganic hazardous waste to TSDF for land filling and organic residue
to TSDF for incineration / cement plants for co-processing.
 The solvent drums shall be kept
on concrete platform only with covered roof. The platform shall be provided with
sufficient dyke wall with leachate collection system.
The solvent drums shall be kept
on concrete platform only with covered roof. The platform shall be provided with
sufficient dyke wall with leachate collection system.
 All the solvent storage tanks shall
be provided with vent condensers to prevent solvent vapour.
All the solvent storage tanks shall
be provided with vent condensers to prevent solvent vapour.
 Transfer of solvents shall be done
by using pumps only instead of manual handling.
Transfer of solvents shall be done
by using pumps only instead of manual handling.
 Proper earthing shall be provided in
all the electrical equipment wherever solvent handling is done.
Proper earthing shall be provided in
all the electrical equipment wherever solvent handling is done.
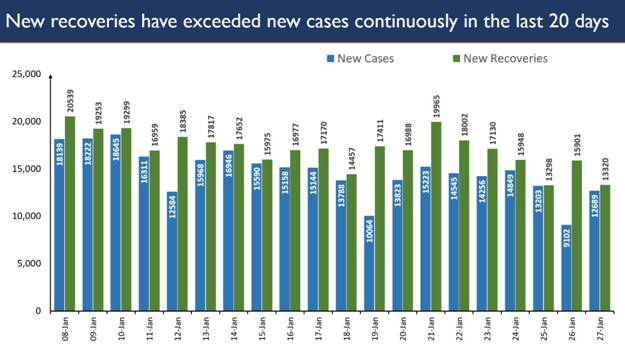
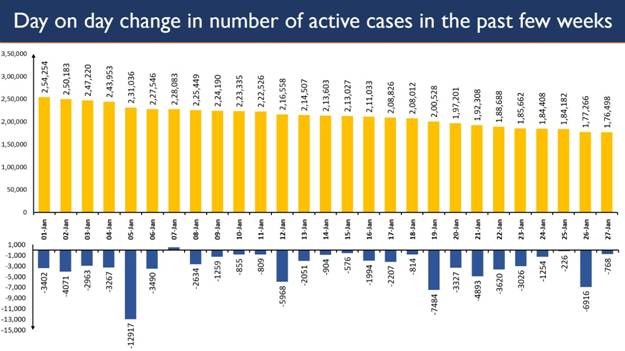
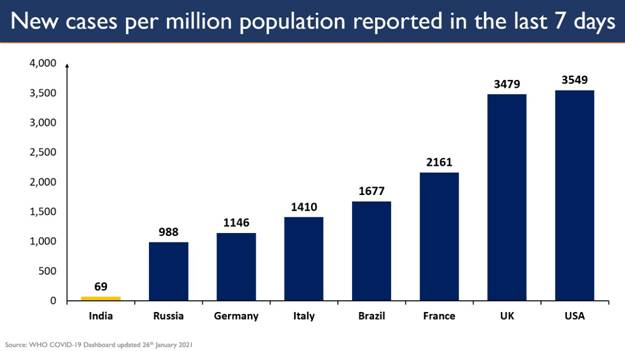
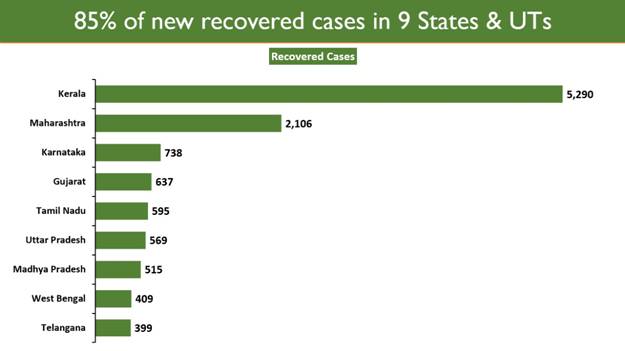











 Guidelines for Industries
Guidelines for Industries







