What is a risk assessment?
Risk assessment is a term used to describe the overall process or method where you:
- Identify hazards and risk factors that have the potential to cause harm (hazard identification).
- Analyze and evaluate the risk associated with that hazard (risk analysis, and risk evaluation).
- Determine appropriate ways to eliminate the hazard, or control the risk when the hazard cannot be eliminated (risk control).
A risk assessment is a thorough look at your workplace to identify those things, situations, processes, etc. that may cause harm, particularly to people. After identification is made, you analyze and evaluate how likely and severe the risk is. When this determination is made, you can next, decide what measures should be in place to effectively eliminate or control the harm from happening.
The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Z1002 Standard "Occupational health and safety - Hazard identification and elimination and risk assessment and control" uses the following terms:
Risk assessment - the overall process of hazard identification, risk analysis, and risk evaluation.Hazard identification - the process of finding, listing, and characterizing hazards.Risk analysis - a process for comprehending the nature of hazards and determining the level of risk.
Notes:
(1) Risk analysis provides a basis for risk evaluation and decisions about risk control.
(2) Information can include current and historical data, theoretical analysis, informed opinions, and the concerns of stakeholders.
(3) Risk analysis includes risk estimation.Risk evaluation - the process of comparing an estimated risk against given risk criteria to determine the significance of the risk.Risk control - actions implementing risk evaluation decisions.
Note: Risk control can involve monitoring, re-evaluation, and compliance with decisions.
For definitions and more information about what hazards and risks are, please see the OSH Answers document Hazard and Risk.
Why is risk assessment important?
Risk assessments are very important as they form an integral part of an occupational health and safety management plan. They help to:
- Create awareness of hazards and risk.
- Identify who may be at risk (e.g., employees, cleaners, visitors, contractors, the public, etc.).
- Determine whether a control program is required for a particular hazard.
- Determine if existing control measures are adequate or if more should be done.
- Prevent injuries or illnesses, especially when done at the design or planning stage.
- Prioritize hazards and control measures.
- Meet legal requirements where applicable.
What is the goal of risk assessment?
The aim of the risk assessment process is to evaluate hazards, then remove that hazard or minimize the level of its risk by adding control measures, as necessary. By doing so, you have created a safer and healthier workplace.
The goal is to try to answer the following questions:
(a) What can happen and under what circumstances?
(b) What are the possible consequences?
(c) How likely are the possible consequences to occur?
(d) Is the risk controlled effectively, or is further action required?
(b) What are the possible consequences?
(c) How likely are the possible consequences to occur?
(d) Is the risk controlled effectively, or is further action required?
When should a risk assessment be done?
There may be many reasons a risk assessment is needed, including:
- before new processes or activities are introduced,
- before changes are introduced to existing processes or activities, including when products, machinery, tools, equipment change or new information concerning harm becomes available, or
- when hazards are identified.
How do you plan for a risk assessment?
In general, determine:
- what the scope of your risk assessment will be (e.g., be specific about what you are assessing such as the lifetime of the product, the physical area where the work activity takes place, or the types of hazards)
- the resources needed (e.g., train a team of individuals to carry out the assessment, the types of information sources, etc.)
- what type of risk analysis measures will be used (e.g., how exact the scale or parameters need to be in order to provide the most relevant evaluation)
- who are the stakeholders involved (e.g., manager, supervisors, workers, worker representatives, suppliers, etc.)
- what relevant laws, regulations, codes, or standards may apply in your jurisdiction, as well as organizational policies and procedures
How is a risk assessment done?
Assessments should be done by a competent person or team of individuals who have a good working knowledge of the situation being studied. Include either on the team or as sources of information, the supervisors and workers who work with the process under review as these individuals are the most familiar with the operation.
In general, to do an assessment, you should:
- Identify hazards.
- Determine the likelihood of harm, such as an injury or illness occurring, and its severity.
- Consider normal operational situations as well as non-standard events such as maintenance, shutdowns, power outages, emergencies, extreme weather, etc.
- Review all available health and safety information about the hazard such as Safety Data Sheet (SDS), manufacturers literature, information from reputable organizations, results of testing, workplace inspection reports, records of workplace incidents (accidents), including information about the type and frequency of the occurrence, illnesses, injuries, near misses, etc.
- Understand the minimum legislated requirements for your jurisdiction.
- Identify actions necessary to eliminate the hazard, or control the risk using the hierarchy of risk control methods.
- Evaluate to confirm if the hazard has been eliminated or if the risk is appropriately controlled.
- Monitor to make sure the control continues to be effective.
- Keep any documents or records that may be necessary. Documentation may include detailing the process used to assess the risk, outlining any evaluations, or detailing how conclusions were made.
When doing an assessment, also take into account:
- The methods and procedures used in the processing, use, handling or storage of the substance, etc.
- The actual and the potential exposure of workers (e.g., how many workers may be exposed, what that exposure is/will be, and how often they will be exposed).
- The measures and procedures necessary to control such exposure by means of engineering controls, work practices, and hygiene practices and facilities.
- The duration and frequency of the task (how long and how often a task is done).
- The location where the task is done.
- The machinery, tools, materials, etc. that are used in the operation and how they are used (e.g., the physical state of a chemical, or lifting heavy loads for a distance).
- Any possible interactions with other activities in the area and if the task could affect others (e.g., cleaners, visitors, etc.).
- The lifecycle of the product, process or service (e.g., design, construction, uses, decommissioning).
- The education and training the workers have received.
- How a person would react in a particular situation (e.g., what would be the most common reaction by a person if the machine failed or malfunctioned).
It is important to remember that the assessment must take into account not only the current state of the workplace but any potential situations as well.
By determining the level of risk associated with the hazard, the employer, and the health and safety committee (where appropriate), can decide whether a control program is required and to what level.
See a sample risk assessment form.
How are the hazards identified?
Overall, the goal is to find and record possible hazards that may be present in your workplace. It may help to work as a team and include both people familiar with the work area, as well as people who are not - this way you have both the experienced and fresh eye to conduct the inspection. In either case, the person or team should be competent to carry out the assessment and have good knowledge about the hazard being assessed, any situations that might likely occur, and protective measures appropriate to that hazard or risk.
To be sure that all hazards are found:
- Look at all aspects of the work.
- Include non-routine activities such as maintenance, repair, or cleaning.
- Look at accident / incident / near-miss records.
- Include people who work off site either at home, on other job sites, drivers, teleworkers, with clients, etc.
- Look at the way the work is organized or done (include experience of people doing the work, systems being used, etc).
- Look at foreseeable unusual conditions (for example: possible impact on hazard control procedures that may be unavailable in an emergency situation, power outage, etc.).
- Determine whether a product, machine or equipment can be intentionally or unintentionally changed (e.g., a safety guard that could be removed).
- Review all of the phases of the lifecycle.
- Examine risks to visitors or the public.
- Consider the groups of people that may have a different level of risk such as young or inexperienced workers, persons with disabilities, or new or expectant mothers.
It may help to create a chart or table such as the following:
| Example of Risk Assessment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task | Hazard | Risk | Priority | Control |
| Delivering product to customers | Drivers work alone | May be unable to call for help if needed | ||
| Drivers have to occasionally work long hours | Fatigue, short rest time between shifts | |||
| Drivers are often in very congested traffic | Increased chance of collision | |||
| Longer working hours | ||||
| Drivers have to lift boxes when delivering product | Injury to back from lifting, reaching, carrying, etc. | |||
How do you know if the hazard will cause harm (poses a risk)?
Each hazard should be studied to determine its' level of risk. To research the hazard, you can look at:
- Product information / manufacturer documentation.
- Past experience (knowledge from workers, etc.).
- Legislated requirements and/or applicable standards.
- Industry codes of practice / best practices.
- Health and safety material about the hazard such as safety data sheets (SDSs), research studies, or other manufacturer information.
- Information from reputable organizations.
- Results of testing (atmospheric or air sampling of workplace, biological swabs, etc.).
- The expertise of an occupational health and safety professional.
- Information about previous injuries, illnesses, near misses, incident reports, etc.
- Observation of the process or task.
Remember to include factors that contribute to the level of risk such as:
- The work environment (layout, condition, etc.).
- The systems of work being used.
- The range of foreseeable conditions.
- The way the source may cause harm (e.g., inhalation, ingestion, etc.).
- How often and how much a person will be exposed.
- The interaction, capability, skill, experience of workers who do the work.
How are risks ranked or prioritized?
Ranking or prioritizing hazards is one way to help determine which risk is the most serious and thus which to control first. Priority is usually established by taking into account the employee exposure and the potential for incident, injury or illness. By assigning a priority to the risks, you are creating a ranking or an action list.
There is no one simple or single way to determine the level of risk. Nor will a single technique apply in all situations. The organization has to determine which technique will work best for each situation. Ranking hazards requires the knowledge of the workplace activities, urgency of situations, and most importantly, objective judgement.
For simple or less complex situations, an assessment can literally be a discussion or brainstorming session based on knowledge and experience. In some cases, checklists or a probability matrix can be helpful. For more complex situations, a team of knowledgeable personnel who are familiar with the work is usually necessary.
As an example, consider this simple risk matrix. Table 1 shows the relationship between probability and severity.
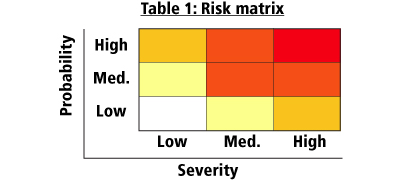
Severity ratings in this example represent:
- High: major fracture, poisoning, significant loss of blood, serious head injury, or fatal disease
- Medium: sprain, strain, localized burn, dermatitis, asthma, injury requiring days off work
- Low: an injury that requires first aid only; short-term pain, irritation, or dizziness
Probability ratings in this example represent:
- High: likely to be experienced once or twice a year by an individual
- Medium: may be experienced once every five years by an individual
- Low: may occur once during a working lifetime
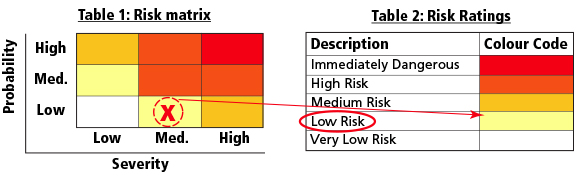
The cells in Table 1 correspond to a risk level, as shown in Table 2.

These risk ratings correspond to recommended actions such as:
- Immediately dangerous: stop the process and implement controls
- High risk: investigate the process and implement controls immediately
- Medium risk: keep the process going; however, a control plan must be developed and should be implemented as soon as possible
- Low risk: keep the process going, but monitor regularly. A control plan should also be investigated
- Very low risk: keep monitoring the process
Let’s use an example: When painting a room, a step stool must be used to reach higher areas. The individual will not be standing higher than 1 metre (3 feet) at any time. The assessment team reviewed the situation and agrees that working from a step stool at 1 m is likely to:
- Cause a short-term injury such as a strain or sprain if the individual falls. A severe sprain may require days off work. This outcome is similar to a medium severity rating.
- Occur once in a working lifetime as painting is an uncommon activity for this organization. This criterion is similar to a low probability rating.
When compared to the risk matrix chart (Table 1), these values correspond to a low risk.
The workplace decides to implement risk control measures, including the use of a stool with a large top that will allow the individual to maintain stability when standing on the stool. They also determined that while the floor surface is flat, they provided training to the individual on the importance of making sure the stool’s legs always rest on the flat surface. The training also included steps to avoid excess reaching while painting.
What are methods of hazard control?
Once you have established the priorities, the organization can decide on ways to control each specific hazard. Hazard control methods are often grouped into the following categories:
- Elimination (including substitution).
- Engineering controls.
- Administrative controls.
- Personal protective equipment.
For more details, please see the OSH Answers Hazard Control.
Why is it important to review and monitor the assessments?
It is important to know if your risk assessment was complete and accurate. It is also essential to be sure that any changes in the workplace have not introduced new hazards or changed hazards that were once ranked as lower priority to a higher priority.
It is good practice to review your assessment on a regular basis to make sure your control methods are effective.
What documentation should be done for a risk assessment?
Keeping records of your assessment and any control actions taken is very important. You may be required to store assessments for a specific number of years. Check for local requirements in your jurisdiction.
The level of documentation or record keeping will depend on:
- Level of risk involved.
- Legislated requirements.
- Requirements of any management systems that may be in place.
Your records should show that you:
- Conducted a good hazard review.
- Determined the risks of those hazards.
- Implemented control measures suitable for the risk.
- Reviewed and monitored all hazards in the workplace.
No comments:
Post a Comment