


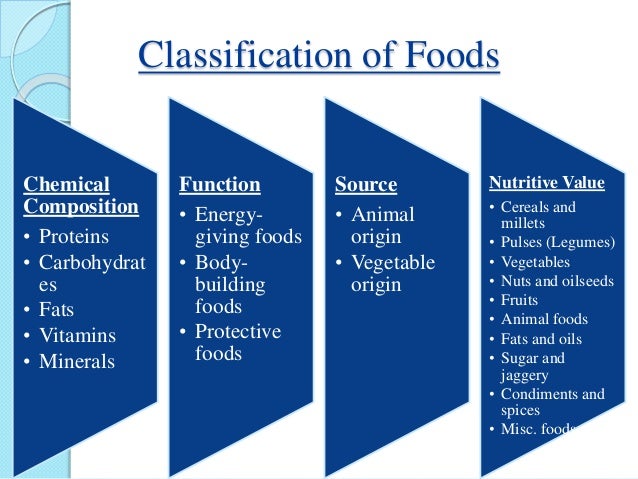
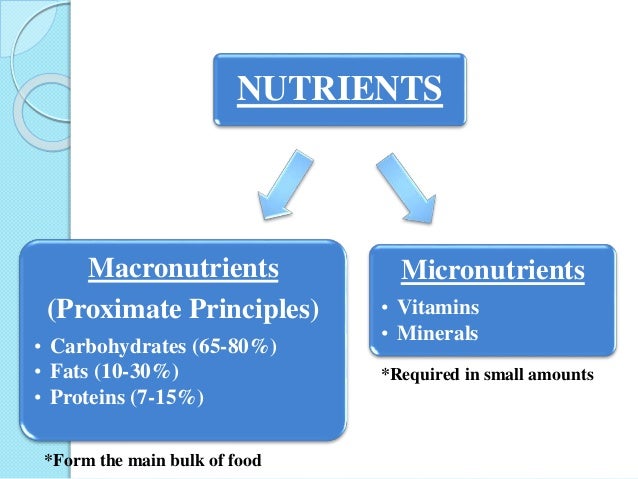

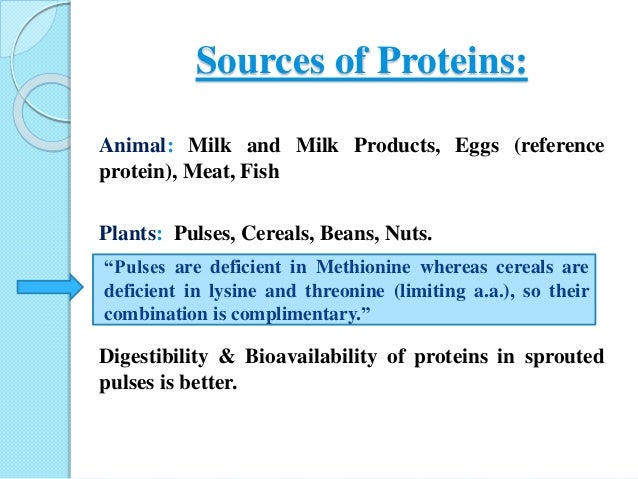
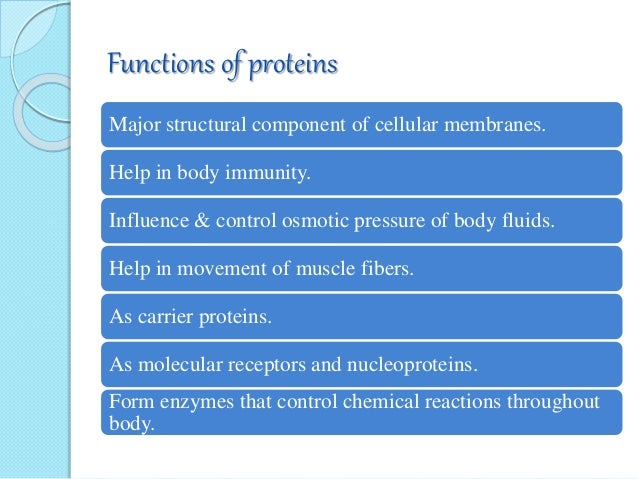
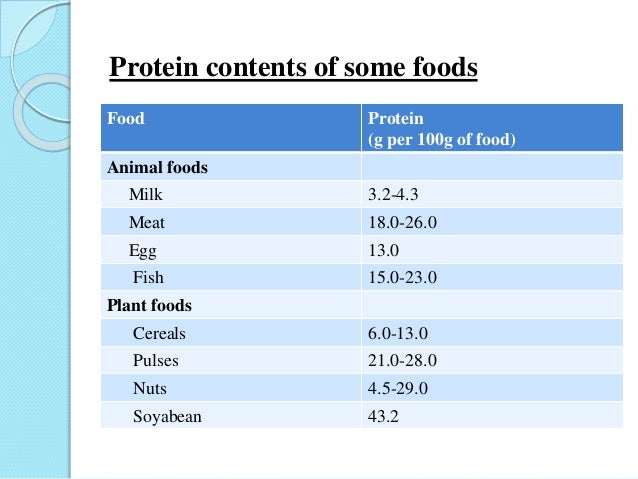

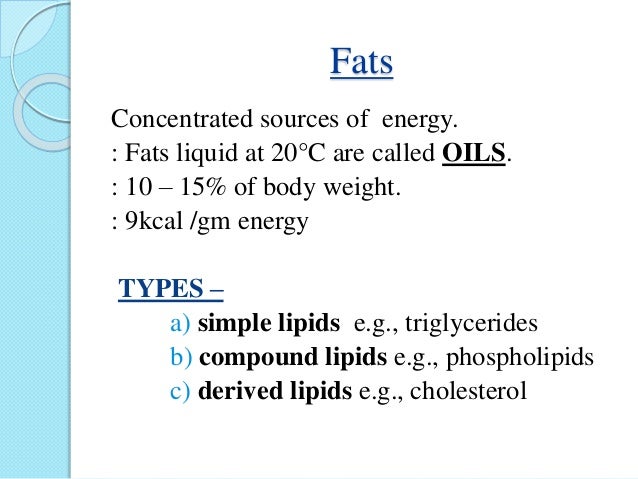


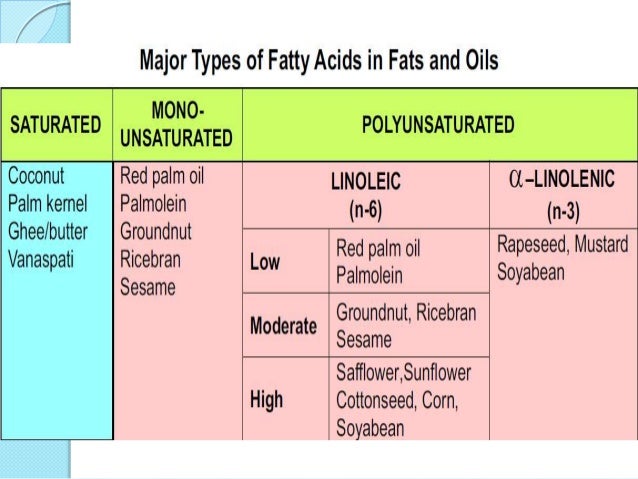
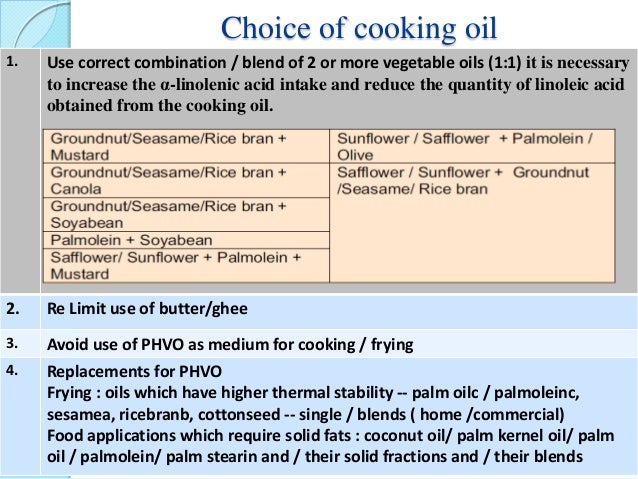







































EHSQL team building , AMGreen and GreenkoGroupFounder Dr. Anil Chalamalasetty and Shri Mahesh Koli Sir,Shri Gautam Reddy,Dr.K.Pradeep,Dr. Rambabu P.,Shri H.Menon,Shri Ch.Srinivas Rao,Shri N. SeshaGiri, Shri GSV Raja,Shri GVS Anand,Shri K.GangadharRao,Shri Madhav KG Shri Satish Babu, Shri Badusha V. Shaik, Shri Srinivas Reddy,Dr.V.S.John,Shri S. Simhachalam, Shri PVSN Raju,Shri B.B.K U.Maheswar Rao,Shri S.Tatayya,Shri S.K. Dash,Shri CH ApplaRaju,Shri LVV Rao EHSQL by Dr.A.N.GIRI-37.5Lakhs Viewed
No comments:
Post a Comment