Electrical Safety Measure To Follow In Industry, Engineer Safety In Industry
Safety is the most important aspect of any industry. The worker’s and employees’ safety should be the first priority before entering the Industrial Plant. Electrical Industries are very dangerous for loss of life if the right precautions are not taken. Electrocution is the major cause of death in Electrical Industries. Electric Fires, Electric Burn & Electric Shock are causes for the Electrical accidents.
Causes Of Electric Accident:
01. Damaged cables & open wiring: The cords get damaged with a time of all electrical appliances, exposing the wires inside. The rubber upon the copper wire gets melted or break if proper care is not taken, which could be the cause for fire or spark. The broken sockets or the weak earthing wire can cause a short circuit in electrical appliances.
02. Wrong cabling & wiring: Faulty wiring or split wires can cause shock and injuries to any person working in the industry. The Electrical wiring should follow the proper sequence and must have proper current handling capability. Overloading many appliances on the same line can cause a high voltage spark.
03. Liquid spillage & moisture: All the electrical connections should be kept away from water and enclosed in the metal enclosure. The appliance near to water should be installed by a professional electrician. The water leakage can cause an electric shock to pass in a large amount.
Important precautions need to take while working in any Industry:-
- Wear proper uniform with helmet and don’t wear loose thing, which can cause accidents. So, it is necessary to wear proper shoes and kit.
- Please stay away from Highly flammable Substances and keep electrical items away from them.
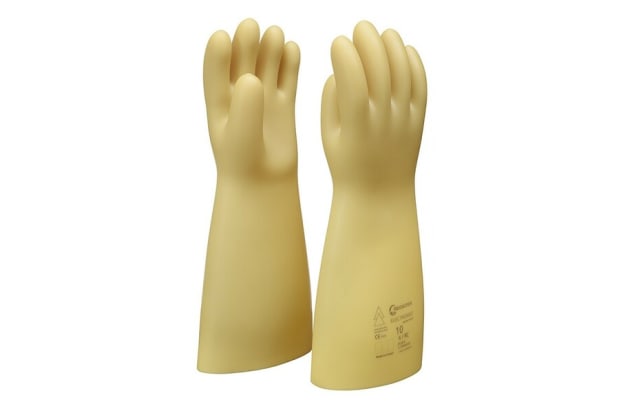
- When working with Electrical Systems, It is compulsory to wear gloves and a safety helmet.
- Stay away from capacitors, Since they are charged it might lead to electric shock.
- Do not touch any electrical conductor, electrical wires, belts, roller, and mechanical moving machines. Shut off the power and then only work on it.
- Keep every Electrical system clean and dust-free, Don’t allow moisture to enter any electrical system. This might lead to the failure of components.
- In Electrical Safety it is always said to work with one hand, which prevents current to pass from the chest cavity.
- Everyone should avoid metal watches, rings, and any conductive metal things. This might result in too heavy a shock.
- Stay away from energized electrical circuits and live.
- Disconnect the Electrical Power supply while installing and servicing electrical machines.
Electrical signs to follow in Industry:-
Engineers and workers must follow these signs at the workplace. Each sign is the caution near the hazard places. A sign such as High voltage means a person should stay away from that place as it is charged with high voltage in KVs. There is a certain hazardous place where entry is restricted because of harmful gases and chemicals.
Electrical Safety Tips for Children
The Dangers of Electricity
Children are naturally curious and do not know the dangers of electricity. Teaching them the basics about the power of electricity and electrical shock helps to keep them safe from harm. The following basics of electricity are important for children to understand.- Electricity has the power to cause burns, shocks and even death.
- Appliances and power cords can be just as dangerous as electrical power lines if you do not take proper safety precautions.
- Electricity flows easily through water, and it will travel through your body since your body is made of 70 percent water.
Electrical Safety Tips for Children
All children, regardless of their age, need to be aware of the dangers of electricity. While the following safety tips are for all children, there are some tips that are more applicable for older children.At Home
- Never stick your fingers or any object into an electrical outlet or light bulb socket.
- Keep fingers and other objects out of small appliances, such as toasters, even if the appliance is off.
- Never use an appliance near a sink, bathtub or other source of water.
- Keep electrical wires and appliance cords away from sources of heat.
- Keep electrical cords away from sinks, bathtubs and other sources of water.
- Never touch any electrical appliance or device, such as a light switch, hair dryer or toaster, if you are touching water.
- Never pull an electric plug out of the wall outlet by yanking on the electric cord.
- Unplug an electrical appliance before cleaning it.
- Never use any electrical appliance if you are wet.
- If you see a worn, frayed or damaged electrical cord, tell an adult immediately.
Outdoors
- Do not climb trees that are near power lines or have power lines running through them.
- If you are flying a kite, or have Mylar or helium-filled balloons on strings, make sure to keep away from power lines. If the kite line or balloon strings are tangled in power lines, the electricity can travel down the line and cause a shock or start a fire.
- Never go swimming during an electrical storm.
- If you see something stuck or tangled in a power line, have an adult call the power company. Never try to remove the item from the power lines yourself.
- Do not climb utility poles.
- Keep away from electric substations.
- Do not climb on fences around electric substations.
- If you see a fallen electrical wire, stay away from it.
- Never touch anything or anyone touching a wire that is down..
- Be careful to avoid touching overhead electrical wires if you are carrying a long object such as a pool skimmer or ladder.
- Never throw objects, such as sneakers, at or onto electric power lines.
- Never touch a power line with any part of your body or any object.
- Never fly model airplanes or remote controlled airplanes or helicopters near overhead power lines. Play with them in open areas such as parks or fields.
- Never go into an electric substation for any reason. If a pet has gone into the area, do not try to get it yourself. Have an adult call the power company.
- Do not hang signs or banners on electric utility poles.
- If you are operating an electrical tool, using an electrical appliance or playing with an electrical toy outside, stay at least 10 feet away from any wet surface or swimming pool.
- Do not touch any electrical tools, appliances or toys if you are wet, standing in a puddle or are in a pool.
FROM MEMORIES Blogger
A Complete Guide to Industrial Electrical Safety
In this guide, we will examine the hazards of electricity in factories and other industrial environments. We will also provide guidance and discuss recommended methods for managing those risks and protecting the health and safety of employees, contractors and visitors alike.
Almost every workplace or factory features electrical items of some kind. If poorly maintained, machinery can cause serious accidents. The risks increase the larger and more powerful the equipment, making electrical safety measures even more important.
To comply with workplace safety requirements, all circuits and wiring must be properly and fully inspected on a regular basis. This is perhaps the single most effective way to protect employees from shocks.
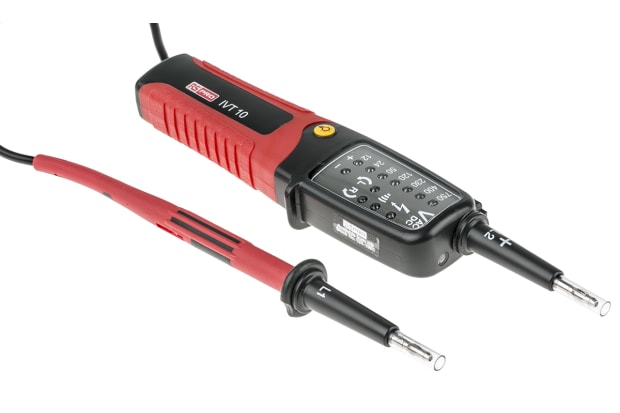
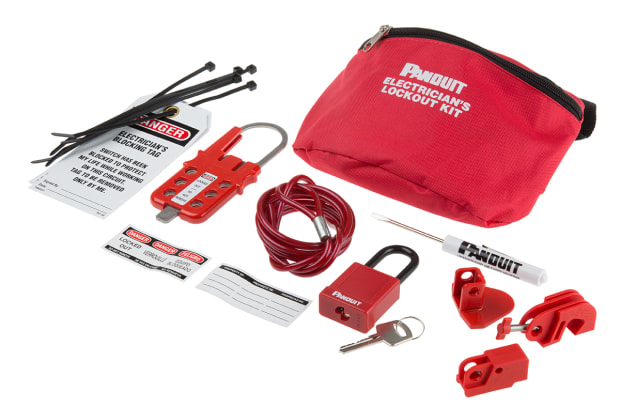
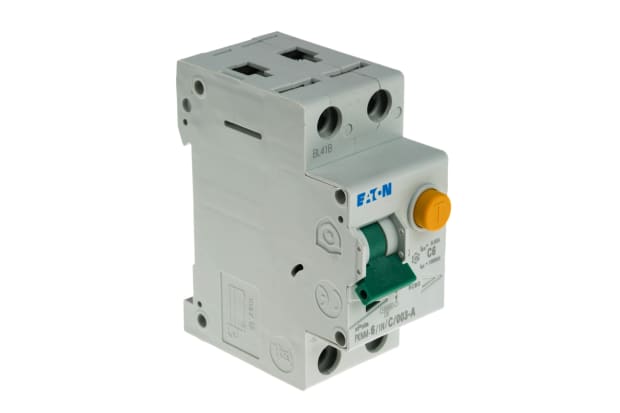
Electrical Safety Equipment
Electrical Safety Regulations
Employers are responsible for ensuring the safety of electrical equipment under the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974. These obligations extend to members of the public who visit or pass the premises. Employers must take ‘all reasonable and practicable steps to prevent danger from electrical systems’.
In January 2019, the BS 7671 (IET Wiring Regulations) came into force. Originally issued by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), these new regulations set a range of electrical safety standards for wiring and electrical installation in the UK. Meanwhile, the Electrical Equipment (Safety) Regulations 2016 impose a range of responsibilities on manufacturers and distributors. Electrical Safety First, formerly known as the Electrical Safety Council, is an active campaigning charity which works to improve regulations and education.
You can find out more about wiring regulations and wiring colours in the UK in our handy guides.
Electrical Safety in the Workplace
Employers should have a comprehensive electrical safety policy in place. Safety training should also be completed in order to ensure that employees are aware of the potential risks they may encounter in their day-to-day roles.
Regular visits by official electrical inspectors from the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) are a must. They will check the safety of on-site equipment and provide advice on good working practice.
A key requirement for employers is to make sure possible electrical hazards in the workplace are frequently assessed and all equipment is safe and fit for purpose. They are required to keep a register documenting these inspections. When issues are identified, suitable repair work should be promptly completed.
Inspection and testing should be carried out by a ‘skilled person or persons, competent in such work’. Normally this 'competent person' implies a qualified and experienced electrical engineer, accredited by a recognised trade body and familiar with applicable codes of practice.
Key potential risks include:
- Isolators and fuse box cases: these should be kept closed and locked whenever possible
- Cables, sockets, plugs and power cords: these must be properly insulated and have sufficient capacity for their use
- Fuses and circuit-breakers: these must be properly matched to the circuit in which they are installed
- Machines and appliances: these must have an off switch that is easy to find and immediately accessible in case of emergency
- Overhead power lines: these should only ever be approached by qualified professionals. Overhead lines are extremely dangerous without the proper precautions
Ask employees to examine electrical equipment before use, looking for damage to plugs or adapters, loose cables and connectors, bare wiring, and similar issues. This is particularly vital for portable equipment which carries a higher risk of incurring damage.
Any issues should be immediately reported, with faulty equipment removed for repair or replacement. Repair work must only be carried out by trained individuals.
Employers failing to meet their legal obligations puts both employees and the business at risk. Faulty electrical equipment is a major cause of fire and if your insurer decides proper electrical safety precautions were not taken, they may refuse to pay out.
Electrical Safety Tips
The key principles of electrical safety at work are:
- Respect live electricity. Touching a live circuit could have fatal consequences
- Conduct regular inspections of equipment. Any electrical equipment should be routinely assessed. Is it still safe to use? Is the cabling properly sealed and insulated? Does it need repair or replacement?
- Ensure correct training. Everyone who uses electrical equipment in the course of their job should be confident in how to use it safely. Nobody should conduct any kind of repairs on electrical equipment without sufficient skills and training
- Do not overload sockets and extension cables as this can cause fires
- Switch off equipment after use and before cleaning or adjusting it in any way
- Check for hidden cables in walls before drilling or inserting nails
- Stop using faulty equipment immediately and have it checked by qualified personnel
- Make sure all equipment in use is suitable for its purpose. Ensure that it remains so via regular electrical safety checks and maintenance
Although the amount and strength of electrical equipment in use varies according to industry, these principles are fundamental and apply more or less equally to hospitals, factories, offices and warehouses.
What are the Main Electrical Risks?
Electricity is dangerous. It can arc across spilt liquid and damp surfaces, it can ignite flammable materials (even gases and dust) to start fires, and it has the potential to cause severe damage to property and equipment. Electric shock can lead to serious injury and fatalities, so the risks should not be ignored. Even relatively minor shocks can cause major injuries.
In the year to 2016, electrical fires caused almost 1,400 serious injuries and fatalities. That equates to around four per day. In 55% of cases, the misuse of electrical equipment was the root cause. More recently, electrical accidents caused four fatalities in UK workplaces during 2018-19.

















No comments:
Post a Comment