We did wonderful discussion with SHRI JK PRAAD SIR
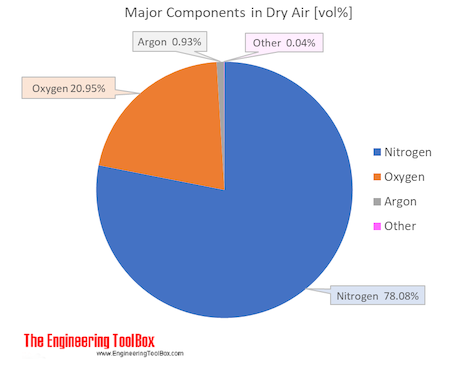
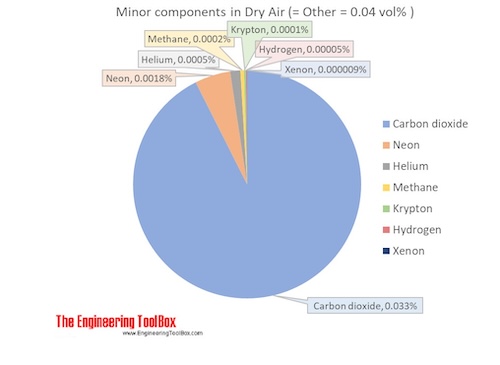
Components in Dry Air
Air is a mixture of several gases, where the two most dominant components in dry air are 21 vol% oxygen and 78 vol% nitrogen. Oxygen has a molar mass of 15.9994 g/mol and nitrogen has a molar mass of 14.0067 g/mol. Since both of these elements are diatomic in air - O2 and N2, the molar mass of oxygen gas is 32 g/mol and the molar mass of nitrogen gas is 28 g/mol.
The average molar mass is equal to the sum of the mole fractions of each gas multiplied by the molar mass of that particular gas:
Mmixture = (x1*M1 + ......+ xn*Mn) (1)wherexi = mole fractions of each gas
Mi = the molar mass of each gas
The molar mass of dry air is 28.9647 g/mol. Composition and content of each gas in air is given in the figures and the table below.


Air is usually modeled as a uniform (no variation or fluctuation) gas with properties averaged from the individual components.
| Components in dry air | Volume ratio = Molar ratio compared to dry air | Molar mass | Molar mass in air | Atmospheric boiling point | |||||
| Name | Formula | [mol/molair] | [vol%] | [g/mol], [kg/kmol] | [g/molair], [kg/kmolair] | [wt%] | [K] | [°C] | [°F] |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 0.78084 | 78.084 | 28.013 | 21.873983 | 75.52 | 77.4 | -195.8 | -320.4 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 0.20946 | 20.946 | 31.999 | 6.702469 | 23.14 | 90.2 | -183.0 | -297.3 |
| Argon | Ar | 0.00934 | 0.934 | 39.948 | 0.373114 | 1.29 | 87.3 | -185.8 | -302.5 |
| Carbon dioxide | CO2 | 0.00033 | 0.033 | 44.010 | 0.014677 | 0.051 | 194.7 | -78.5 | -109.2 |
| Neon | Ne | 0.00001818 | 0.001818 | 20.180 | 0.000367 | 0.0013 | 27.2 | -246.0 | -410.7 |
| Helium | He | 0.00000524 | 0.000524 | 4.003 | 0.000021 | 0.00007 | 4.2 | -269.0 | -452.1 |
| Methane | CH4 | 0.00000179 | 0.000179 | 16.042 | 0.000029 | 0.00010 | 111.7 | -161.5 | -258.7 |
| Krypton | Kr | 0.0000010 | 0.0001 | 83.798 | 0.000084 | 0.00029 | 119.8 | -153.4 | -244.0 |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 0.0000005 | 0.00005 | 2.016 | 0.000001 | 0.000003 | 20.3 | -252.9 | -423.1 |
| Xenon | Xe | 0.00000009 | 0.000009 | 131.293 | 0.000012 | 0.00004 | 165.1 | -108.1 | -162.5 |
| Average molar mass of air | 28.9647 | ||||||||
- The water or vapor content in air varies. The maximum moisture carrying capacity of air depends primarily on temperature
- The composition of air is unchanged until elevation of approximately 10.000 m
- The average air temperature diminishes at the rate of 0.6oC for each 100 m vertical height
- "One Standard Atmosphere" is defined as the pressure equivalent to that exerted by a 760 mm column of mercury at 0oC sea level and at standard gravity (32.174 ft/sec2)
Other components in air
- Sulfur dioxide - SO2 - 1.0 parts/million (ppm)
- Nitrous oxide - N2O - 0.5 parts/million (ppm)
- Ozone - O3 - 0 to 0.07 parts/million (ppm)
- Nitrogen dioxide - NO2 - 0.02 parts/million (ppm)
- Iodine - I2 - 0.01 parts/million (ppm)
- Carbon monoxide - CO - 0 to trace (ppm)
- Ammonia - NH3 - 0 to trace (ppm)
Common Pressure Units frequently used as alternative to "one Atmosphere"
- 76 Centimeters (760 mm) of Mercury
- 29.921 Inches of Mercury
- 10.332 Meters of Water
- 406.78 Inches of Water
- 33.899 Feet of Water
- 14.696 Pound-Force per Square Inch
- 2116.2 Pounds-Force per Square Foot
- 1.033 Kilograms-Force per Square Centimeter
- 101.33 kiloPascal
No comments:
Post a Comment