Difference between BOD and COD and characteristics of Domestic Waste Water in terms of BOD and COD
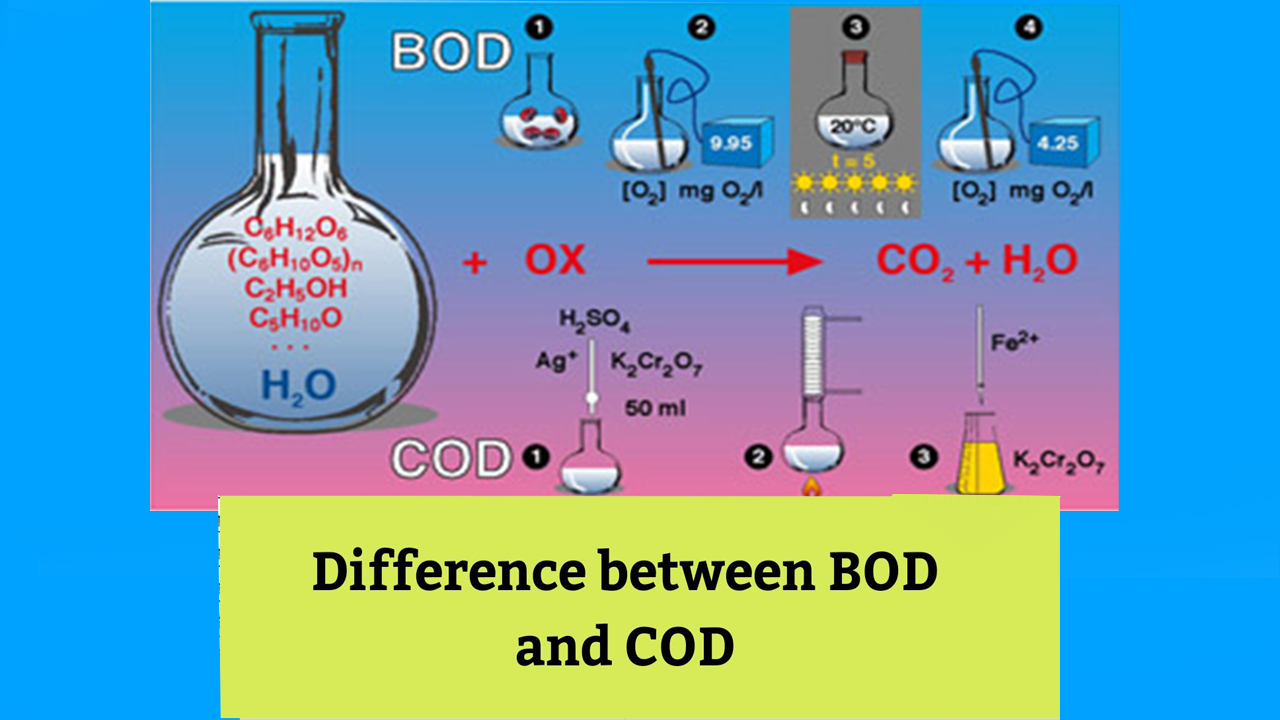
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Biological Oxygen demand (BOD) are the two major characteristic and properties that indicate the strength of sewage. Both the parameters are used to test the oxygen-demanding strength by the wastewaters.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
The amount of oxygen that’s required for the chemical oxidation of the organic and inorganic chemicals present within the wastewater by utilizing oxidizing agents like permanganate of potash , salt etc. is named as chemical oxygen demand (COD). The presence of COD facilitates rapid chemical oxidation of organic matter with none additional equipment. this is often the sole method that permits to work out the organic load in heavy toxic sewage.
To determine COD, the sample water is taken during a closed container and incubated with a robust oxidant like salt with vitriol under standard conditions of temperature and time. COD is that the oxygen demand that’s consumed by both inorganic and organic matter present within the wastewater sample. The chemical oxygen demand is expressed because the mass of oxygen consumed over the quantity of the answer . Its SI unit is milligrams per liter (mg/l).
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD)
BOD is defined because the amount of oxygen demanded by the micro-organisms within the sewage for the decomposition of bio-degradable matter under aerobic condition. this is often the foremost commonly used parameter to work out the strength of municipal or organic quality of the water.
Measurement Unit of BOD
The standard BOD test determines the quantity of oxygen required by the micro-organisms for the decomposition of the bio-degradable matter present within the wastewater sample under 5 days of aerobic condition at a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius. it’s measured in mg/l.
BOD is decided for designing treatment facilities. it’s wont to determine the dimensions of activated sludge units and trickling filter units. it’s also wont to determine the efficiency of varied treatment units.
Difference between Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD)
BOD measures the quantity of oxygen required by the aerobic organisms to decompose organic matter and COD measures the oxygen required to decompose organic and inorganic constituents present within the wastewater by reaction . Hence, the worth of COD is bigger than BOD.
The basic differences between BOD and COD are enlisted within the table below.
Difference between BOD and COD
| BOD | COD |
| BOD is a biological oxidation process | COD is a chemical oxidation process |
| BOD is performed by aerobic organisms | COD is performed by chemical reagents |
| BOD is measured by keeping a sealed water sample for incubation for a period of 5 days at 20 degree Celsius. The reduction in dissolved oxygen gives the amount of oxygen consumed by the aerobic organisms. | In COD test, the water sample is incubated with a strong oxidant in combination with boiling sulphuric acid for a specific period of time and temperature. |
| BOD value is determined by 5 days. | COD can be measured within few days. |
| BOD value is lower than COD | COD value is always greater than BOD |
| BOD is used to oxidize the natural organic matter and organic waste in the water | COD is capable of degrading the industrial sewage. COD does not measure the amount of oxygen consumed by acetates present in the water sample |
Based on the strength of BOD and COD present, the domestic wastewater are often classified as weak, medium, strong and really strong as shown in table-2 below. The strength given is predicated on the water consumed per person.
What is the characteristics of Domestic Waste Water in terms of BOD and COD
| Classification | BOD (mg/l ) | COD (mg/l ) |
| Weak | <200 | <400 |
| Medium | 350 | 700 |
| Strong | 500 | 1000 |
| Very Strong | >750 | >1500 |
For any waste water treatment related product Inquiry please call Netsol Water
No comments:
Post a Comment