| Horticulture :: Plantation Crops :: Tea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Varieties
Pandian, Sundaram, Golconda, Jayaram, Evergreen, Athrey, Brookeland, BSS 1, BSS 2, BSS 3, BSS 4, BSS 5, Biclonal seed stocks and Grafts.
Healthy and vigorously growing high yielding bushes should be selected. Apply to each selected bush with 40 g of young tea mixture + 60:90 NK mixture up to 5 years. The following mixture has to applied before taking the cuttings.
Preparation of cuttingsCuttings are taken on April - May and August - September. Semi hard-wood cuttings are prepared with one leaf and an internode with a slanting cut at the bottom.
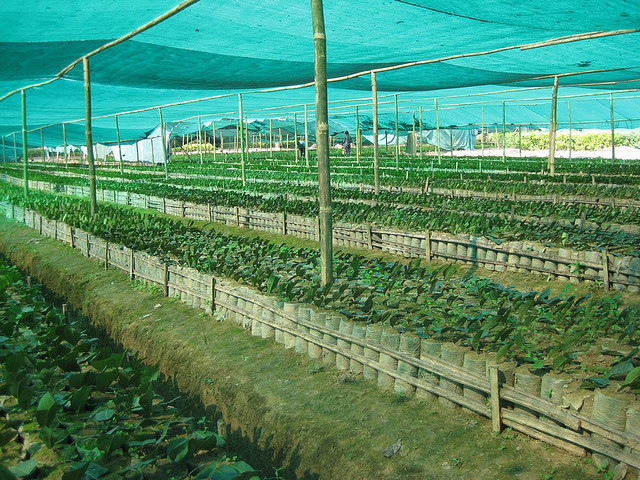
Planting of cuttings
The sleeves are watered thoroughly and holes are made in the soil. The cuttings are inserted in the hole and the soil around is pressed firmly to avoid airspace followed by watering. Small polythene tents may be provided which maintain high humidity and regulate the temperature inside. Cuttings may take 10 - 12 weeks for rooting. After 90 days i.e. when all the cuttings have rooted, the polythene tent may be removed gradually over a period of 10 - 15 days.
Manuring of nursery
After the tent is removed the cuttings are sorted and staked. 30 g of Nursery soluble mixture of the following composition dissolved in 10 litres of water may be applied over an area of 4 sq.m. This should be done fortnightly.
Composition of the fertilizer
Ammonium phosphate (20:20) 35 parts by Wt Potassium sulphate 15 parts by Wt (or) MOP 12 parts by Wt Magnesium sulphate 15 parts by Wt Zinc sulphate 3 parts by Wt Total 80 parts by Wt
Hardening of the cuttings
Hardening of 4 - 6 months old young cuttings should be done by removing shade gradually in stages over a period of 4 - 6 weeks starting from a few hours exposure to sun every day initially and extending the time of exposure gradually.
Manuring should be done 2 months after planting. Phosphorous should be applied at 80 - 100 kg/ha as Rock phosphate once in a year by placement at 15 - 25 cm depth up to the first pruning and thereafter once in two years. N : K ratio 2 : 3 should be adapted for the first 3 years and a ratio 1 : 1 thereafter.
Application of fertilizers should be done before the onset of monsoon. Fertilizers should be broadcast around the drip circle avoiding contact with the collar.
Aftercultivation
Perennial grasses (Forbicot weeds) can be controlled by spraying Glyphosate 1.75 lit + Kaoline 2 lit + 2 kg of wetting agent in 450 lit. of water followed by Gramoxone 500 ml in 200 lit of water to control dicot weeds.
Training young tea
Centering To induce more laterals, centering should be done 3 - 5 months after planting. The main leader stem should be cut, leaving 8 - 10 matured leaves.
Tipping
Tipping is done at a height of 35 cm from the second tipping at 60 cm from ground level.
Pruning
Pruning is done to maintain convenient height of bush and to remove dead and diseased branches. Area to be pruned every year = Total extent of the garden Pruning cycle Pruning interval = (Elevation in feet / 1000) + 1 Pruning should be done in April - May or August - September.
Types of pruning
Rejuvenation pruning The whole bush should be cut near the ground level less than 30 cm with a view to rejuvenate the bushes.
Hard pruning
Hard/ formation pruning of young tea is done at 30 to 45 cm (12" to 18") for proper spread of bushes.
Medium pruning
To check the bush growing to an inconvenient height this type of pruning is done in order to stimulate new wood and to maintain the foliage at lower levels less than 60 cm.
Light pruning
Pruning depends on the previous history of the bush raising the height of medium pruning by an inch or less to manageable heights for plucking (less than 65 cm).
Skiffing
This is the lightest of all pruning methods. A removal of only the top 5 - 8 cm new growth is done so as to obtain a uniform level of pruning surface (more than 65 cm).
Shade regulation
Pollarding of shade trees should be done prior to heavy rains at a height of 8 - 10 m from the ground level.
Annual lopping
Cutting the erect type branches on the laterals in shade trees before monsoon season.
Plant protection
Sahydrassis / Phassus borerScales Scales can be controlled by spraying Carbaryl 50 WP @ 2 g/lit. or Quinalphos 25 EC @ 2 ml/lit or Chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 2 ml/lit. Locate the particle mat covering at the base tea bush and remove. Insert a thick wire in the bore hole to kill the larvae. Thrips Spray any one of the following insecticide
Spray phosalone 35 % EC @ 2.0 ml/lit Red spider mite, Pinkmite, scarlet mite
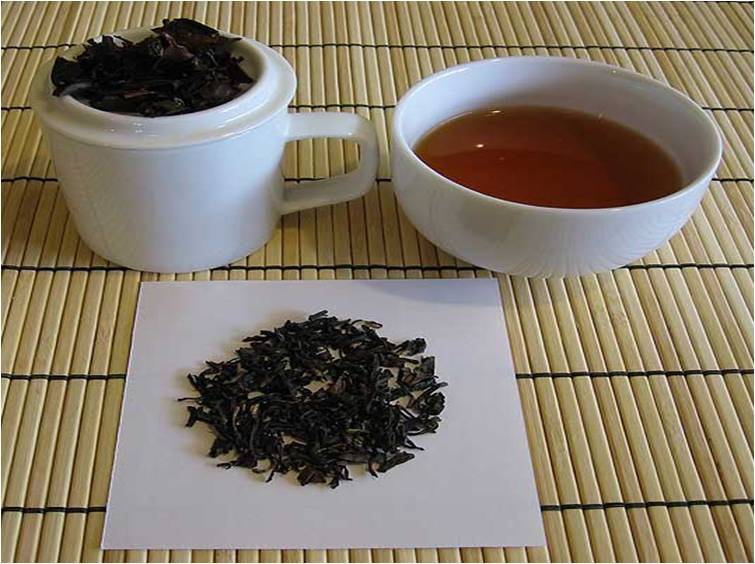
   Banji bud Harvesting in tea
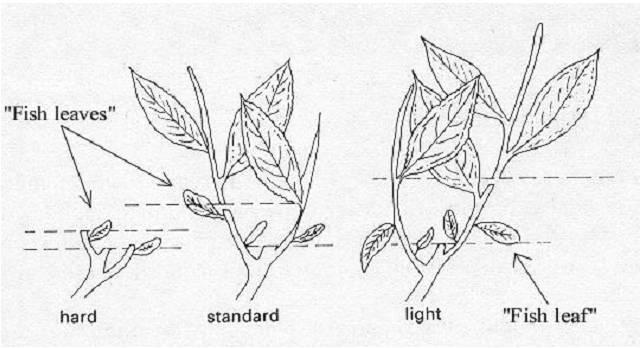
Plucking commences when the tea bush is 3 years old. The plucking of extreme tip of the growing branch consists of an unopened bud together with two leaves is popularly known as "Two leaves and a bud", while fine plucking is anything less than this. In South India plucking continues throughout the year at weekly intervals during March - May and at intervals of 10 -14 days during the other months.
Rush period
During rush period harvesting is done at 7 to 10 days interval.
Lean period
During lean period harvesting is done at 10 – 15 days interval.
Yield
The yield of green leaves is 10 t/ha
Market Information
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dedicated Team spirit, Knowledge Sharing session and thanks to Greenko Founder, MD and CEO Shri Chalamalasetty Sir and Founder & president Shri Mahesh Koli SIr, AM Green management Shri Gautam Reddy, Shri GVS ANAND, Shri VIJAY KUMAR (Site Incharge), Shri G.B.Rao, Shri PVSN Raju, Dr. V. S. John, Shri V. Parmekar,Smt .Vani Tulsi,Shri B.B.K UmaMaheswar Rao, Shri P. Rajachand, Shri V. B. Rao, Shri. LVV RAO, Shri P.Srinivaslu Promotion- EHSQL-by Dr. A.N.GIRI- 29.1Lakhs Viewed Thanks to NFCL.
Wednesday, 23 May 2018
Tea (Camellia sinensis L. O. Kuntze.) Camelliaceae
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)






















No comments:
Post a Comment