What is a Dobson Unit?
The Dobson Unit is the most common unit for measuring ozone concentration. One Dobson Unit is the number of molecules of ozone that would be required to create a layer of pure ozone 0.01 millimeters thick at a temperature of 0 degrees Celsius and a pressure of 1 atmosphere (the air pressure at the surface of the Earth). Expressed another way, a column of air with an ozone concentration of 1 Dobson Unit would contain about 2.69x1016ozone molecules for every square centimeter of area at the base of the column. Over the Earth’s surface, the ozone layer’s average thickness is about 300 Dobson Units or a layer that is 3 millimeters thick. Seen from space, the edge of the Earth is blurred by the pale
blue atmosphere. Most dense at the surface, the atmosphere
thins with altitude, until it gradually merges with vacuum.
Total ozone is measured through the entire atmospheric
column, from the surface to the edge of space.
Seen from space, the edge of the Earth is blurred by the pale
blue atmosphere. Most dense at the surface, the atmosphere
thins with altitude, until it gradually merges with vacuum.
Total ozone is measured through the entire atmospheric
column, from the surface to the edge of space.
The average amount of ozone in the atmosphere is roughly 300 Dobson Units, equivalent to a layer 3 millimeters (0.12 inches) thick—the height of 2 pennies stacked together. What scientists call the Antarctic Ozone “Hole” is an area where the ozone concentration drops to an average of about 100 Dobson Units. One hundred Dobson Units of ozone would form a layer only 1 millimeter thick if it were compressed into a single layer, about the height of a dime.
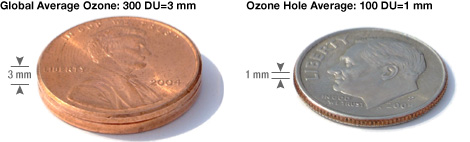 Compressed to sea-level pressure, the ozone in the atmosphere
would form a layer about the height of two pennies stacked
together. Levels in the ozone hole are much less—only
the height of a single dime.
Compressed to sea-level pressure, the ozone in the atmosphere
would form a layer about the height of two pennies stacked
together. Levels in the ozone hole are much less—only
the height of a single dime.
No comments:
Post a Comment