However, a more serious problem arises capture operation as a
result of the combination of the amines from the absorption liquid with
the nitrogen oxides (NO) from the flue gas from the combustion plant.
Even though the concentration of nitrogen oxides in the flue gas is
comparatively low, amines with nitrogen oxides form nitrosamines
(N-nitroso compounds) which are carcinogenic to living organisms
directly, through degradation products or via side reactions. The
nitrosamines formed may have a low vapor pressure, and they can
therefore also be discharged into the atmosphere via the cleaned flue
gas.
Only the nitrosamines formed from secondary amines are stable for any period. The primary nitrosamines react further to give alkenes and alcohols (Lehrbuch der organischen Chemie [Organic Chemistry]; Beyer and Walter, 1991), which are much less of a concern than the carcinogenic nitrosamines. Tertiary amines can react to give stable nitrosamine compounds only through their decomposition products, secondary amines. The reason why secondary amines are nevertheless preferred over the primary amines in CO2 capture plants is the lower binding energy and hence a lower loss of efficiency in the overall power plant.
EHSQ , NFCL
M.Sc. -Environmental Science,Ph.D -Environmental Science law & DIPLOMA AS - P.G.D.E.P.L,CES, DCA,
EX IIM LUCKNOW FELLOW, EX RESEARCH SCIENTIST
IGIDR-MUMBAI
9912511918
amarnathgiri@nagarjunagroup.com
http://www.nagarjunagroup.com
http://www.nagarjunafertilizers.com
EHSQ BLOG : http://dramarnathgiri.blogspot.in/?view=magazine
http://dramarnathgiri.blogspot.in/2013/10/curriculum-vitae-of-dr-amar-nath-giri.html?q=BIO+DATA
http://dramarnathgiri.blogspot.in/2012/05/nagarjuna-management-services.html
Only the nitrosamines formed from secondary amines are stable for any period. The primary nitrosamines react further to give alkenes and alcohols (Lehrbuch der organischen Chemie [Organic Chemistry]; Beyer and Walter, 1991), which are much less of a concern than the carcinogenic nitrosamines. Tertiary amines can react to give stable nitrosamine compounds only through their decomposition products, secondary amines. The reason why secondary amines are nevertheless preferred over the primary amines in CO2 capture plants is the lower binding energy and hence a lower loss of efficiency in the overall power plant.
With best regards,
Moreover, secondary amines exhibit a much higher loading capacity for CO2 compared to primary amines. Tertiary amines have the disadvantage that they react very slowly with carbon dioxide and thus require large columns.
In the case of gas scrubbing in the chemical industry, there is usually no occurrence of the problem since the nitrosating substance (nitrogen dioxide, or nitrogen monoxide which is to be oxidized to nitrogen dioxide) is generally not present, as a result of which there is also no possibility of nitrosation. In some operations, for example the tire industry, inhibitors are deliberately added to the operation in order to prevent the formation of the N-nitroso components. In the food industry, there are some known and effective inhibitors, for example selenium. However, the acidic medium present therein differs distinctly from the alkaline conditions in the CO2 deposition.
In an advantageous configuration, the secondary amine is an amino acid salt. In a further advantageous configuration, the salt of vitamin C is sodium ascorbate. Amino acid salts have the advantage over other amines, such as alkanolamines, sterically hindered amines or amino acids, that they do not have any noticeable vapor pressure. The inventive solvent can be employed particularly advantageously in the case of amino acid salts, since the subsequent purification or the destruction of the stable nitrosamines is much more difficult in the case of amino acid salts than in comparison to conventional amines such as the alkanolamines or sterically hindered amines. In the case of alkanolamines, one option is distillation for the purification. Due to the lack of vapor pressure, in contrast, this is not possible for amino acid salts. These can be separated from the nitrosamines only by crystallization of the salt.
Nitrous acid is a Brønsted acid of moderate strength (pKa = 3.3). Because it is unstable, it is prepared immediately before use in the following manner:
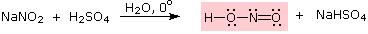
Under the acidic conditions of this reaction, all amines undergo reversible salt formation:
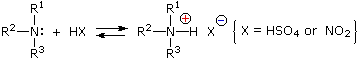
This happens with 3º-amines, and the salts are usually soluble in
water. The reactions of nitrous acid with 1°- and 2°- aliphatic amines
may be explained by considering their behavior with the nitrosonium
cation, NO(+), an electrophilic species present in acidic nitrous acid solutions.

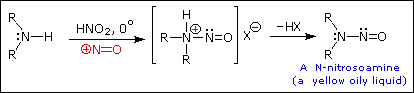
"Seven Billion Dreams. One Planet. Consume with Care."
(2015)
Dr. AMAR NATH GIRIMoreover, secondary amines exhibit a much higher loading capacity for CO2 compared to primary amines. Tertiary amines have the disadvantage that they react very slowly with carbon dioxide and thus require large columns.
In the case of gas scrubbing in the chemical industry, there is usually no occurrence of the problem since the nitrosating substance (nitrogen dioxide, or nitrogen monoxide which is to be oxidized to nitrogen dioxide) is generally not present, as a result of which there is also no possibility of nitrosation. In some operations, for example the tire industry, inhibitors are deliberately added to the operation in order to prevent the formation of the N-nitroso components. In the food industry, there are some known and effective inhibitors, for example selenium. However, the acidic medium present therein differs distinctly from the alkaline conditions in the CO2 deposition.
In an advantageous configuration, the secondary amine is an amino acid salt. In a further advantageous configuration, the salt of vitamin C is sodium ascorbate. Amino acid salts have the advantage over other amines, such as alkanolamines, sterically hindered amines or amino acids, that they do not have any noticeable vapor pressure. The inventive solvent can be employed particularly advantageously in the case of amino acid salts, since the subsequent purification or the destruction of the stable nitrosamines is much more difficult in the case of amino acid salts than in comparison to conventional amines such as the alkanolamines or sterically hindered amines. In the case of alkanolamines, one option is distillation for the purification. Due to the lack of vapor pressure, in contrast, this is not possible for amino acid salts. These can be separated from the nitrosamines only by crystallization of the salt.
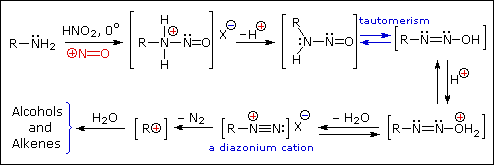
Reaction of Amines with Nitrous Acid
Nitrous acid (HNO2 or HONO) reacts with aliphatic amines in a fashion that provides a useful test for distinguishing primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
|
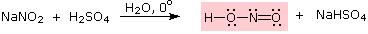


Primary Amines

Secondary Amines
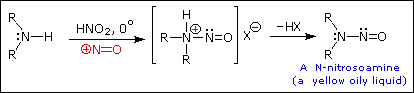
"Seven Billion Dreams. One Planet. Consume with Care."
(2015)
M.Sc. -Environmental Science,Ph.D -Environmental Science law & DIPLOMA AS - P.G.D.E.P.L,CES, DCA,
EX IIM LUCKNOW FELLOW, EX RESEARCH SCIENTIST
IGIDR-MUMBAI
9912511918
amarnathgiri@nagarjunagroup.com
http://www.nagarjunagroup.com
http://www.nagarjunafertilizers.com
http://dramarnathgiri.blogspot.in/2013/10/curriculum-vitae-of-dr-amar-nath-giri.html?q=BIO+DATA
http://dramarnathgiri.blogspot.in/2012/05/nagarjuna-management-services.html

No comments:
Post a Comment