Politics of global warming
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
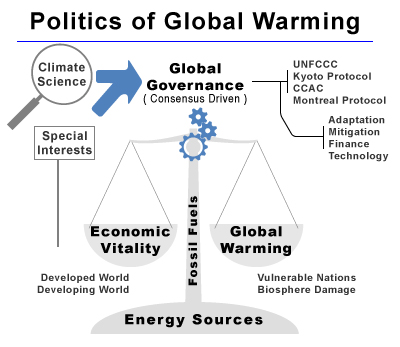
The politics of global warming
are very complex due to numerous factors that arise from the global
economy's complex interdependence on carbon dioxide emitting hydrocarbon
energy sources and carbon dioxide being directly implicated in global
warming - making global warming a non-traditional / non-conventional
environmental challenge and its politics extremely complex:- Implications to all aspects of a nation-state's economy - A consensus of the world's scientists attribute global warming to the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases which implicates almost every aspect of a nation-state's economy because the vast majority of the world's economy relies on energy sources or manufacturing techniques that release greenhouse gases at almost every stage of production, transportation, storage, delivery & disposal;
- Perceived lack of adequate advanced energy technologies - Fossil fuel abundance and low prices continue to put pressure on the development of adequate advanced energy technologies that can realistically replace the role of fossil fuels - over 91% of the worlds energy is derived from fossil fuels and non carbon-neutral technologies. Developing countries do not have cost effective access to the advanced energy technologies that they need for development (most advanced technologies has been developed by and exist in the developed world). Without adequate and cost effective post-hydrocarbon energy sources, it is unlikely the countries of the developed or developing world would accept policies that would materially affect their economic vitality or economic development prospects;
- Industrialization of the developing world - Developing nations have only recently started to industrialize and their carbon dioxide emissions are beginning to rise at a time when the scientific community is telling the world that carbon dioxide emissions should be decreasing (without access to cost effective and abundant energy sources many developing countries see climate change as an oppressor that is keeping them from developing naturally);
- Metric selection (transparency) and perceived responsibility / ability to respond - Disagreements exist over which greenhouse gas emission metrics should be used like total emissions per year, per capita emissions per year, CO2 emissions only, deforestation emissions, livestock emissions or even total historical emissions. The release of carbon dioxide has not been historically even among all nation-states and nation-states have challenges with determining who should restrict emissions and at what point of their industrial development they should be subject to such commitments;
- Vulnerable developing countries and developed country legacy emissions - Some developing nations fix blame on the developed world for having created the challenge because it was the developed countries that emitted most of the carbon dioxide over the twentieth century and they perceive that it should be the developed countries that should pay to address the challenge;
- Consensus-driven global governance models - The global governance bodies that evolved during the 20th century are all consensus driven deliberative forums where agreement is difficult to achieve and even when it is achieved almost impossible to enforce;
- Well organized and funded special-interest lobbying bodies - Special interest lobbying by well organized groups distort and amplify aspects of the challenge (environmental lobbying, energy industry lobbying, other special interest lobbying);
- Politicization of climate science - Although there is a consensus on the science of global warming and its likely effects - some special interests groups work to suppress the consensus while others work to amplify the alarm of global warming. All parties that engage in such acts add to the politicization of the science of global warming. The result is a clouding of the reality of global warming.
No comments:
Post a Comment